Event Manager
The Event Manager is a feature that gives the ability to streamline workflows between the UX and third-party platforms/services on predefined system Events. The Event Manager allows for easy control, defining and managing of Actions that will be triggered upon those events (For example: This feature may be useful to those that have a requirement to trigger a webhook for answered and unanswered calls, so that they may execute internal automation on call analytics, and similar situations).
The event manager is divided into 3 sections, Events, Actions and Parameters.
Events
The Events page is devised into 3 tabs, Event List, Settings and Activity Montor.
The Event List tab displays the list of predefined system events, their description as well as their status. Available system Events are:
- Incoming Call
- Answered Call
- Unanswered Call
- Hangup
- Ringing
Event List

Predefined events cannot be deleted, but they can be edited. To edit any of the events, click on the event’s name or the edit icon on the far right. This will open the Event edit page with two available options:

| Actions | Active |
|---|---|
| Select one or more actions (previously created) you want to trigger when the event occurs from the dropdown. | This option allows you to enable or disable actions for this specific event. |
Settings
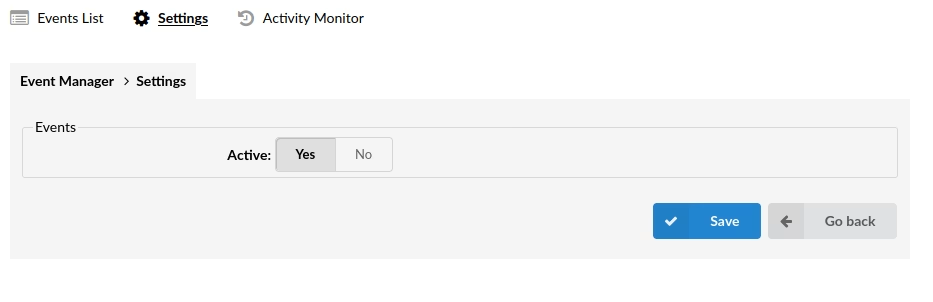
The Settings tab allows the administrator to Enable or Disable actions for all events. By default, actions for all the Events are globally disabled, so all the events on the Event List page will have their active status grayed out in the Active column. Changing the Active option to Yes will enable actions for all active events.
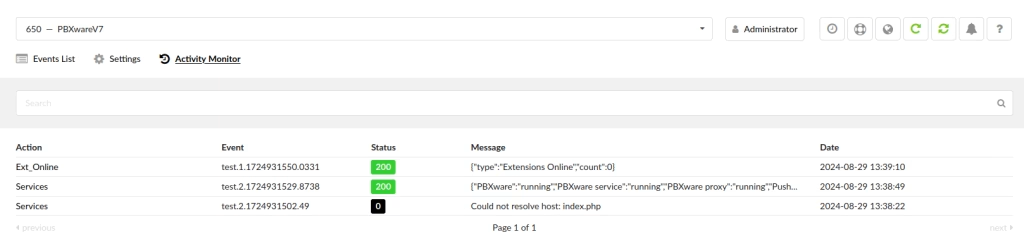
Activity Monitor
List of all events triggered from the system or the tested ones. There will be status and message displayed about the action that was triggered.
Actions
The Actions page allows an administrator to define an HTTP request that can be attached to an Event and sent once the event is triggered. A single Action can be attached to multiple events.
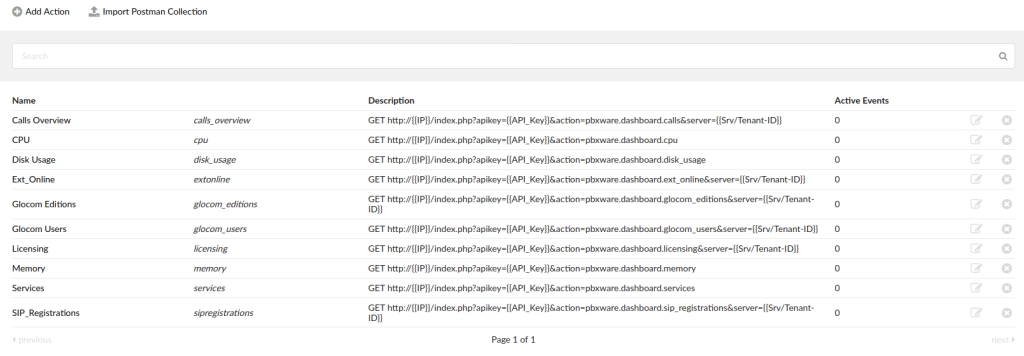
| Add Action | Import Postman Collection | Search |
|---|---|---|
| Creates a new Action | Allows you to import your Postman collection | Allows you to search your actions |
Add Action
This option allows you to create (or edit) an action directly on the PBX. There are many options that allow an administrator to customize this feature to accommodate their needs.
 |
GeneralName: Unique name assigned to the individual actions. Description: A short description of the action specifics. HTTP Method: HTTP method refers to the type of HTTP request used to send data from the webhook source to the webhook consumer. Available options:
|
- PATCH requests will make only partial updates to the data on the target server.
- DELETE requests indicate that certain data should be removed.
- URLThe address to which HTTP requests will be sent.
Query
Key: The key is the name or identifier associated with a particular parameter. It serves as the reference point used by the webhook consumer to identify and extract the corresponding value from the query string. Keys are typically alphanumeric strings and may contain special characters but must adhere to URL encoding rules. For example, in the query string ?name=John&age=30, “name” and “age” are the keys.
Value: The value is the actual data or information associated with the key. It represents the content or value assigned to a specific parameter within the query string. Values can vary in format and content, depending on the webhook consumer’s requirements and the parameter’s purpose. Continuing with the previous example, “John” is the value associated with the “name” key, and “30” is the value associated with the “age” key.
Body
Type: None
None typically indicates that the webhook does not include a message body in the HTTP request.
This means that the webhook provider sends data to the consumer without including any payload in the request body. Instead, the relevant information is conveyed through other means, such as HTTP headers or query parameters.
- Form-data
When sending data using form data, the payload is typically formatted as a series of key-value pairs, similar to how data is submitted in an HTML form. Each key-value pair represents a field and its corresponding value. This format is commonly used when the webhook provider wants to mimic the behavior of submitting a form.
- x-www-form-urlencoded
When using x-www-form-urlencoded format in webhooks, the payload is structured similarly to form data, where each key-value pair is encoded in a specific way to conform to the application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type. This format is commonly used when a webhook provider sends data to a webhook consumer in a structured yet simple manner.
- raw
This means that the payload of the webhook request is sent exactly as provided by the webhook source without any additional processing or formatting by the webhook provider.
A “raw” body type allows for flexibility in the content of the webhook payload. It means that the webhook provider does not enforce any specific format for the payload, leaving it up to the webhook consumer to handle and parse the data according to its requirements.
Authorization
No Auth
Select No Auth if the endpoint requires no authorization.
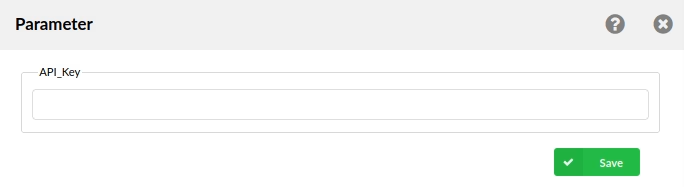
API Key
This option indicates that API Key will be sent along with the webhook request. The webhook consumer validates the API key to ensure the request comes from an authorized source.
Basic Auth
Basic authentication requires a username and password to be sent with the webhook request. The webhook consumer validates the credentials before processing the request.
Bearer Token
Some webhook providers may use custom tokens for authentication purposes. These tokens are unique to the provider and consumer and are used to validate the authenticity of the webhook request.
Header
Headers
In the context of webhooks, headers consist of key-value pairs that provide additional information about the HTTP request being sent from the source to the webhook endpoint.
Key
The key refers to the name or identifier of a specific header in an HTTP request sent as part of a webhook. Headers are key-value pairs included in the HTTP request’s header section, providing additional information about the request or specifying how the server should handle it.
Value
refers to the content associated with a specific header key in an HTTP request sent as part of a webhook.
Undefined Parameters
When editing an action that was previously created, if you have parameters that have not been defined in the parameters tab of the Event Manager but they are being used in that specific action, they will be listed at the top of the action page with the option to add them along with their assigned value.
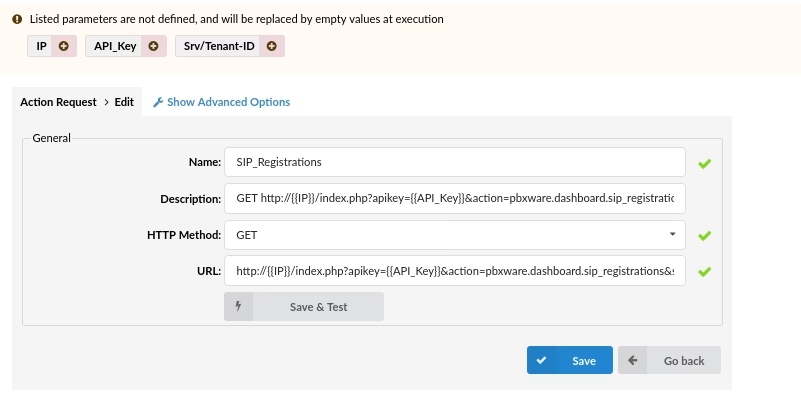
Click on the parameter in order to add it to the parameters list where you will be prompted to assign a value to it as well.
Import Postman Collection
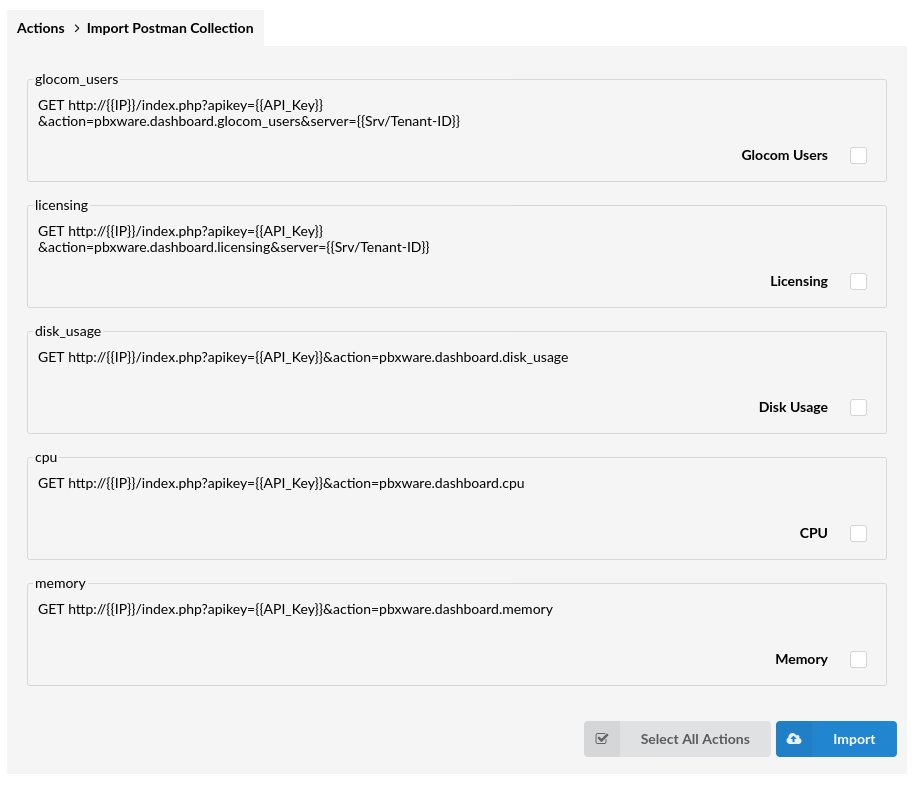
This option enables an administrator to import collections they already have stored in Postman. After a collection is imported, all of the available requests will appear on the list, from where they can be selected one by one or by using Select all Actions, followed by the Import button to complete the procedure.
Parameters
The Parameters section defines the system and custom parameters the admin can create and use inside Actions. Defined by ‘tag’ and ‘value’. Parameters used in Actions are only replaced when a request is sent, so throughout system, the parameter tag will be shown. To use a Parameter in Action, it needs to be defined with a tag enclosed by double curly brackets, like: {{parameter_tag}} The system default parameters can be found in the list on the Parameters page with the cog (cog) icon and are the following:
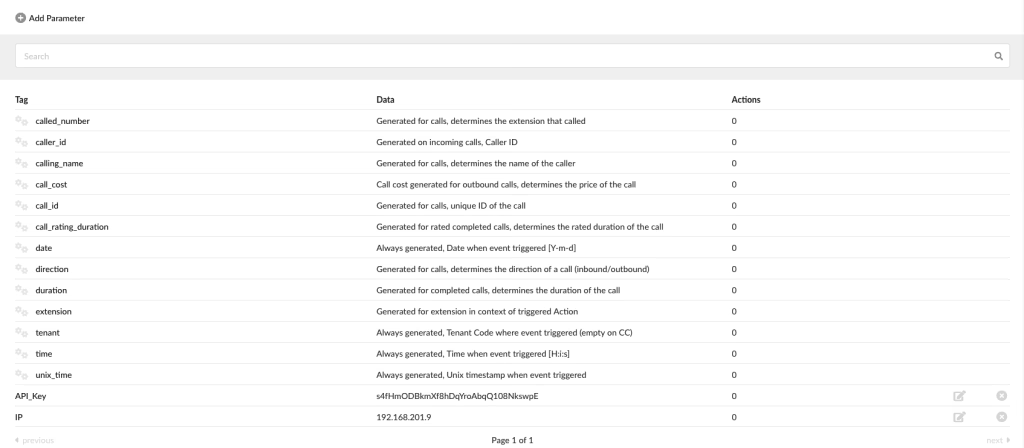
- called_number – Generated for calls, determines the extension that called
- caller_id – Generated on incoming calls, Caller ID
- calling_name – Generated for calls, determines the name of the caller
- call_cost – Call cost generated for outbound calls, determines the price of the call
- call_id – Generated for calls, a unique ID generated for calls
- call_rating_duration – Generated for rated completed calls, determines the rated duration of the call
- date – Always generated, Date when event was triggered [Y-m-d]
- direction – Generated for calls, determines the direction of a call (inbound/outbound)
- duration – Generated for completed calls, determines the duration of the call
- extension – Generated for extension in the context of triggered Action
- tenant – Always generated, Tenant Code where event triggered (empty on CC)
- time – Always generated, Time when an event triggered [H:i:s]
- unix_time – Always generated, Unix timestamp when an event was triggered. These default parameters cannot be deleted or edited.